Basic Concepts of Neuropharmacology
Learn about the Basic Concepts of Neuropharmacology. The nervous system, types, and classification of the nervous system.
Nervous System
CNS
(Central Nervous System) - Include brain & spinal cord
PNS
(Peripheral Nervous system) Peripheral
of brain and spinal cord
It has 2 division.
ANS
(Autonomic Nervous System) - Work
based on autonomic control.
Somatic
Nervous System - Work
based on our control.
ANS
It
also has two division.
Sympathetic
works
in emergency condition like fight & flight.
e.g. Dilation of pupil, Heart rate
increase etc.
Parasympathetic
works
in normal condition as in resting.
e.g.
Constriction of pupil, Heart rate decrease, Salivation etc.
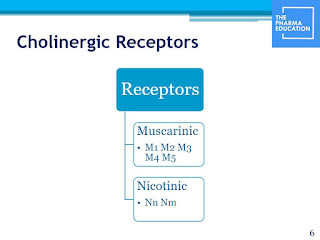
Parasympathetic
System
It has main neurotransmitter as
Acetylcholine that bind to cholinergic receptor.
The drugs that mimic the action of
Acetylcholine known as Parasympatho-mimetic drugs.
The drugs that block the action of
Acetylcholine known as Parasympatho-lytic drugs.
Sympathetic
System
It
has main neurotransmitter as Adrenaline that bind to Adrenergic receptor.
The
drugs that mimic the action of Adrenaline known as Sympatho-mimetic drugs.
The
drugs that block the action of Adrenaline known as Sympatho-lytic drugs.
Neurotransmitters
in CNS
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
GABA, Glycine, Dopamine
(Inhibitory effect on CNS)
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Glutamate, Aspartate
(Stimulatory effect on CNS)
Acetylcholine, Noradrenaline, Serotonin (5HT)
(Mediate both inhibitory as well as excitatory effects)
IPSP
(Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential)
(Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential)
When
an inhibitory transmitter binds & interacts with specific receptors on postjunctional
membrane, the membrane permeability to K or Cl
increases.
K
ions move out and Cl ions move in resulting in
hyperpolarization (IPSP)
EPSP
(Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential)
(Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential)
When
an excitatory transmitter binds & interacts with specific receptors on postjunctional
membrane, the membrane permeability to cations
increases.
Na
ions move in (Na influx) resulting in depolarization followed by K efflux.